1. A thief stole a box with valuable article of weight ‘W’ and jumped down a wall of height h. Before he reach the ground he experienced a load of
2. The acceleration due to gravity g and mean density of the earth r are related by which of the following relation? Where g is gravitational constant and R is radius of the earth
3. When the planet comes nearer the sun moves
4. Kepler’s second law regarding constancy of arial velocity of a planet is a consequence of the law of conservation of
5. The period of geostationary artificial satellite is
6. A geostationary satellite is orbiting the earth at a height of 6R above the surface of the earth, R being the radius of the earth. The time period of another satellite at a height of 2.5 R from the surface of earth is
7. The distance of Neptune and Saturn from the sun are nearly 1013 m and 1012 m respectively. Assuming that they move in circular orbits, their periodic times would be in the ratio of
8. A satellite is orbiting close to the surface of the earth, then its speed is
9. If the gravitational force between two objects were proportional to 1/R (and not as 1/R2) where R is separation between them, then a particle in circular orbit under such a force would have its orbital speed v proportional to
(d) T
2 a R
3
11. The period of a satellite in a circular orbit of radius R is T. The period of another satellite in circular orbit of radius 4R is
(a) T/4
(b) 8T
(c) 2T
(d) T/8
12. A planet moves around the sun. At a point A, it is closest from the Sun at a distance d1 and has a speed v1. At another point B, when it is farthest from the sun at a distance d2, its speed will be
(a)
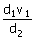
(b)
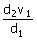
(c)
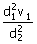
(d)
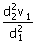
13. The period of geostationary artificial satellite of earth is
(a) 6 hours
(b) 12 hours
(c) 24 hours
(d) 365 days
14. If ‘r’ represents the radius of the orbit of a satellite of mass ‘m’ moving round a planet of mass ‘M’, the velocity of the satellite is given by
(a) v
2 =
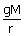
(b) v
2 =
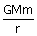
(c) v =
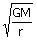
(d) v =
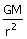
15. A missile is launched with a velocity less than the escape velocity. The sum of its kinetic and potential energy is
(a) Positive
(b) Negative
(c) Zero
(d) may be positive or negative
16. The escape velocity of projection from the earth is approximately (R = 6400 km)
(a) 7 km/sec
(b) 112 km/sec
(c) 12.2 km/sec
(d) 1.1 km/sec
17. If the earth is 1/4th of its present distance from the sun, the duration of the year would be
(a) 1/4 of the present year
(b) 1/6 of the present year
(c) 1/8 of the present year
(d) 1/16 of the present year
18. The relation between escape velocity and orbit velocity is
(a) v
e =
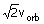
(b) v
e =
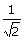
v
orb
(c) ve = 2vorb
(d) v
e =
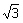
v
orb
19. There is no atmosphere on the moon because
(a) it is closer ot the earth
(b) it revolves round the earth
(c) it gets light from the sun
(d) the escape velocity of gas molecules is less than their root mean square velocity here
20. If the radius of the earth were to shrink by 1% its mass remaining the same, the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface would
(a) decrease by 2%
(b) remain unchanged
(c) increase by 2%
(d) will increase by 9.8%
21. Fg and Fe represents gravitational and electrostatic forces respectively, between the two electrons situated at a distance of 10 m. The ratio Fg/Fe is of the order of
(a) 1043
(b) 1036
(c) 10-43
(d) 10-36
22. The value of ‘g’ at a particular point is 9.8 m/sec2 suppose the earth suddenly shrink uniformly to half its present size without losing any mass. The value of ‘g at the same point (assuming that the distance of the point from the centre of the earth does not shrink) will become
(a) 9.8 m/sec2
(b) 4.9 m/sec2
(c) 19.6 m/sec2
(d) 2.45 m/sec2
23. The planet mercury is revolving in an elliptical orbit around the sun as shown in figure. The kinetic energy of mercury will be greater at
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
24. The orbit velocity of an artificial satellite in a circular orbit just above the earth’s surface is v. For a satellite orbiting at an altitude of half of the earth’s radius, the orbital velocity is
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

25. If the change in the value of g at the height h above the surface of the earth is the same as at a depth x below it, then (both x and h being much smaller than the radius of the earth)
(a) x = h
(b) x = 2 h
(c) x =

(d) x = h2
